Established in 2022 under the leadership of Selçuk Bayraktar, Fergani Space is a technology company operating in the space sector with commercial satellites, satellite components, payloads and orbit transfer vehicles (OTVs) powered by indigenous propulsion technology.


With its newly developed low-orbit satellite constellation architecture, Fergani Space aims to provide multi-band communication and positioning services with global coverage.
The company continues its work on operating platforms, equipment, and payloads under orbital conditions within this scope. In response to the growing demand for satellite services, Fergani is focusing on low-cost and highly efficient constellation solutions, an approach based on the coordinated operation of multiple small satellites rather than a single large one. This model allows the system capacity to be scaled in a flexible manner.
Micro-Satellite Characteristics
The features of the micro-satellite constellation that the company has deployed into low Earth orbit are as follows:
- Mass: in the 100 kg class
- Altitude: to operate in the 500–600 km range
- Payloads: to support various missions such as communication and geolocation
- Communication Bands: global coverage in Ku, Ka, S, and L bands
- Ground Segment: ground segment infrastructure enabling tracking, management, and communication of the satellite constellation will also be established by Fergani
- Applications: beyond geolocation, it aims to provide innovative solutions for global needs in maritime, aviation, Internet of Things (IoT), meteorology, and logistics
FGN-100-d1
The FGN-100-d1 satellite was launched into orbit on January 14, 2025, at 22:09 (UTC +3) from Vandenberg Space Force Base in the United States via the Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
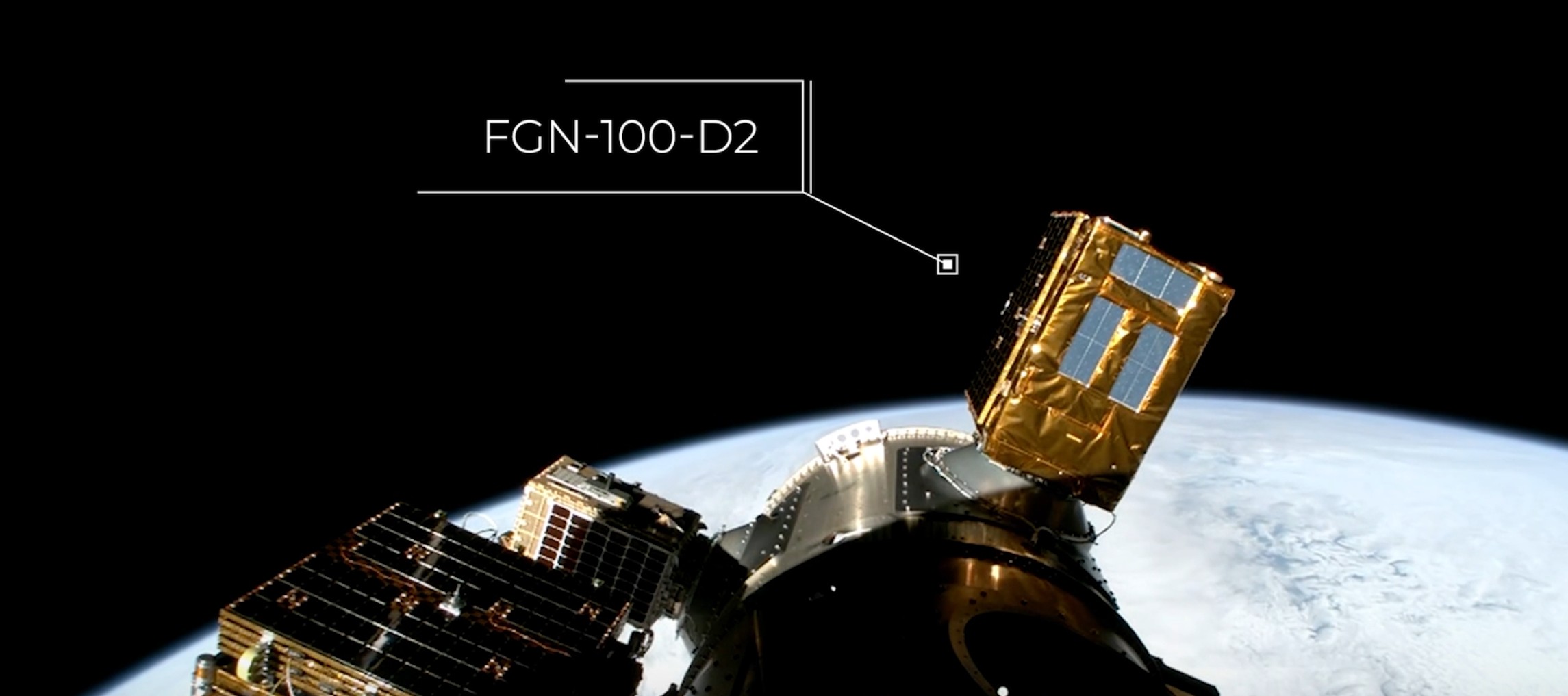
FGN-100-d2
FGN-100-d2 was launched into orbit on November 2, 2025, at 08:09 (UTC +3) from the Cape Canaveral SLC-40 launch facility as part of the Bandwagon-4 mission.

Fergani is developing an Orbit Transfer Vehicle (OTV) using domestic hybrid rocket propulsion technology to provide a highly efficient and cost-effective solution that maximizes orbital transfer capability.
Importance and Function
Traditional launch systems carry tons of payload into predefined orbits. However, satellite operators’ target orbits do not always match these launch plans. In such cases, operators must either wait for a compatible launch window or conduct a custom launch at high cost, both of which result in time loss and increased expense.
Fergani’s OTV solution eliminates this problem by providing flexibility: operators can participate as secondary payloads in launch programs compatible with their schedules and reach their target orbits after arriving in space thanks to the OTV.
Technological Features
Fergani uses indigenous hybrid rocket propulsion technology to maximize the orbital transfer capability of the OTV. This innovative and cost-effective solution increases in-space maneuverability, enhancing the operational efficiency of satellites.
- Time and Cost Savings: Enables faster and more economical access to target orbits
- Operational Flexibility: Ability to adapt to different launch programs
- Increased Efficiency: Plays an active role in all maneuvers required throughout a satellite’s operational life
FGN-TUG-S01 Orbit Transfer Vehicle
On 28 November 2025, Türkiye’s first Orbit Transfer Vehicle, FGN-TUG-S01, developed entirely with national capabilities by Fergani Space Technologies, was successfully launched from the US Vandenberg Space Force Base aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 Transporter-15 rocket.
The Uluğ Bey Global Positioning System is a positioning project based on low-orbit satellite constellations developed entirely with domestic engineering capabilities by Fergani Space.
Once completed, the system aims to establish a national navigation and timing network capable of operating independently of foreign GNSS architectures.
With the implementation of the Uluğ Bey Positioning System, Türkiye aims to become the fifth country to develop its own global positioning system, following the United States, Russia, China, and the European Union.
The main objective of the project is to create a satellite constellation of over 100 satellites within five years and to make the system operational both in Türkiye and in friendly and partner countries.